1. The Early Days: Rubber and Aluminum Hoses
In the early days of industrialization, hoses were primarily made from rubber and, later, aluminum. These materials were chosen for their availability and ease of manufacturing.
Rubber Hoses: Rubber was one of the first materials used for hose production due to its flexibility and elasticity. However, rubber hoses were limited by their lack of durability and susceptibility to chemical and temperature changes.
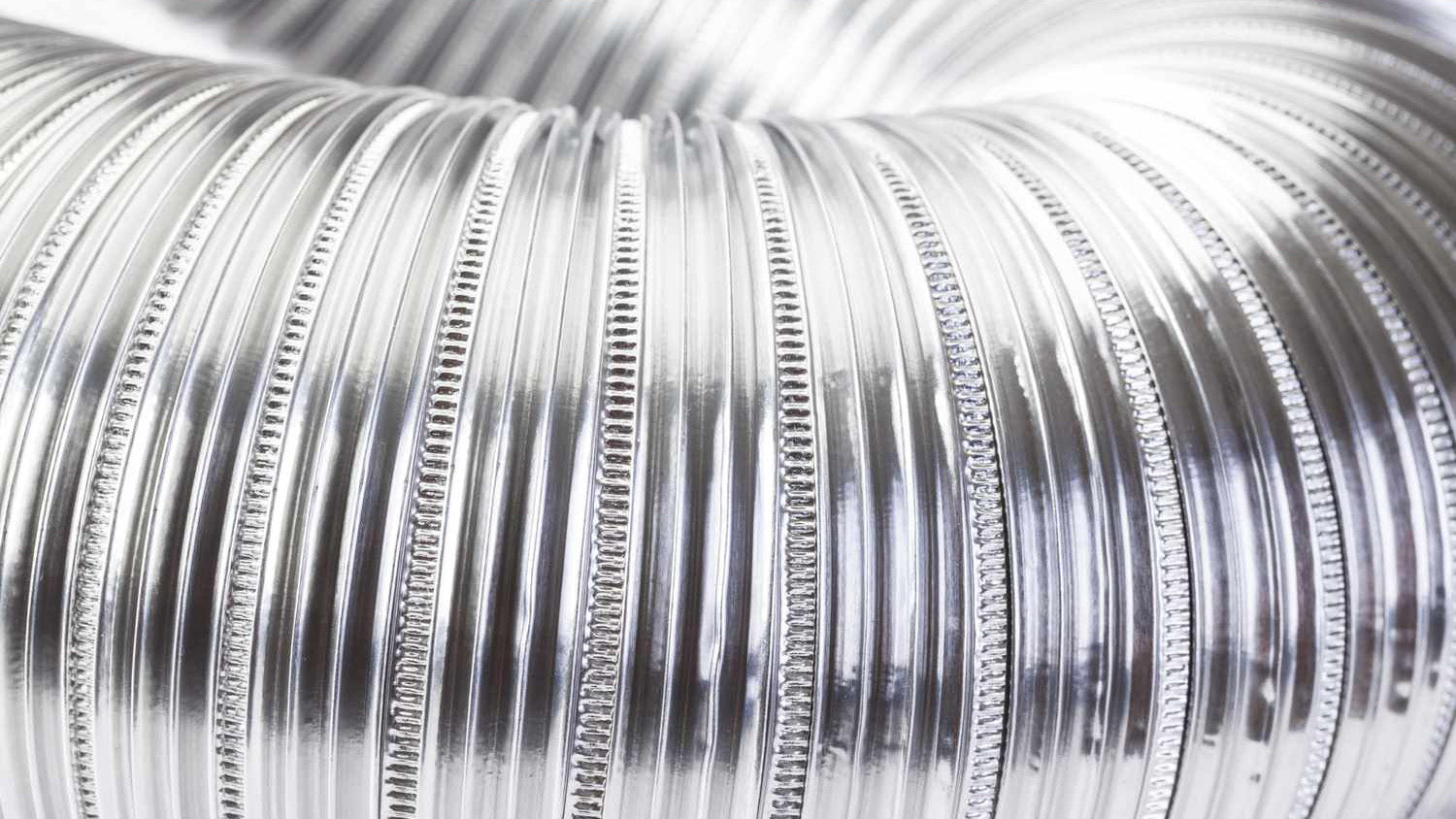
Aluminum Hoses: The introduction of aluminum offered a lightweight alternative with better resistance to corrosion and temperature. Aluminum hoses became popular in applications requiring moderate chemical resistance and flexibility.
2. Limitations of Aluminum Hoses
While aluminum hoses provided certain advantages over rubber, they also had significant limitations that prompted the search for better materials.
Corrosion Issues: Although more resistant to corrosion than rubber, aluminum hoses could still corrode when exposed to certain chemicals, especially acids and bases.
Lower Strength: Aluminum, while lightweight, did not offer the high tensile strength required for more demanding industrial applications.
3. The Rise of Stainless Steel Hoses
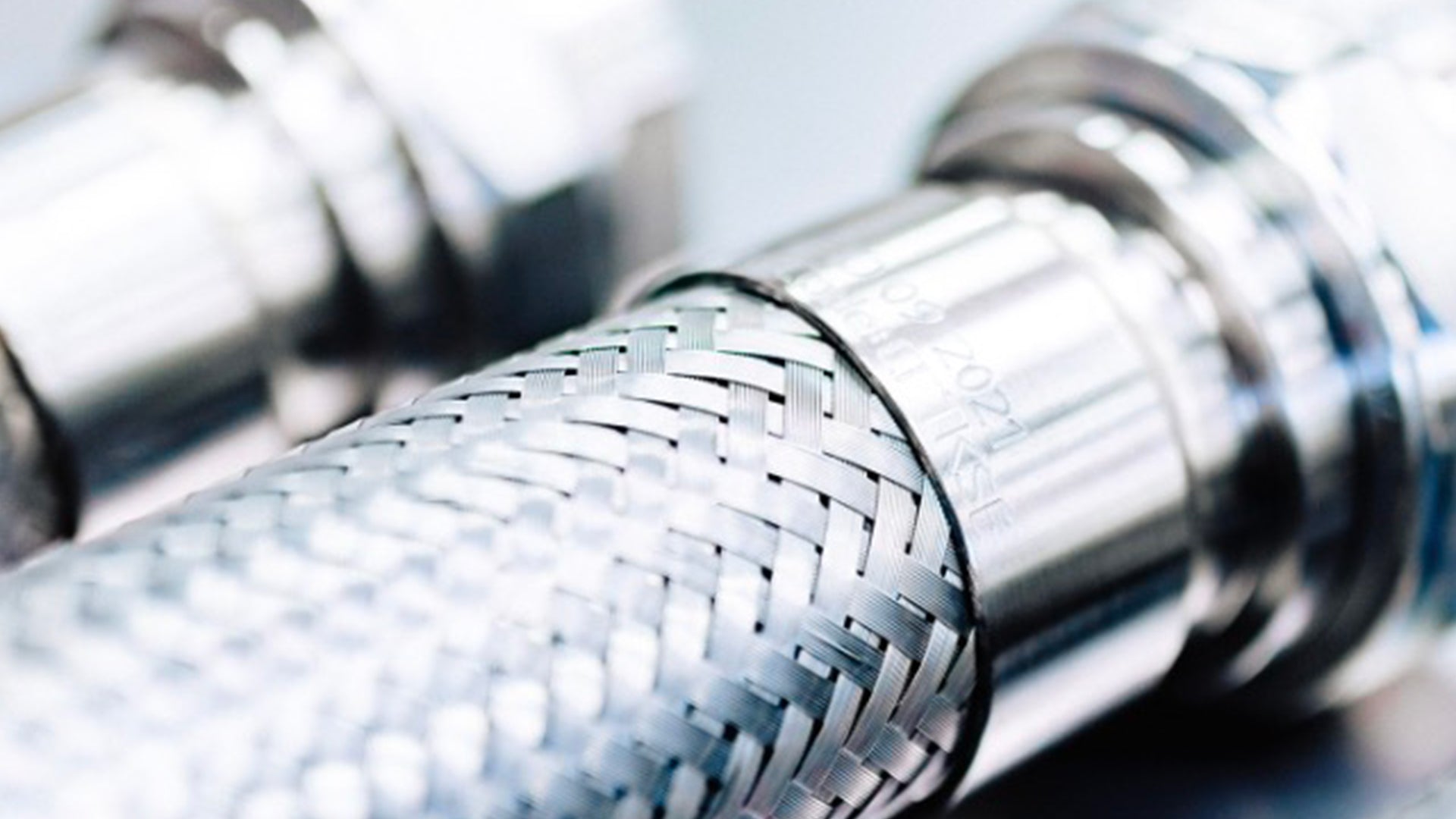
The limitations of aluminum led to the development and widespread adoption of stainless steel hoses, which offered several superior properties.
Exceptional Durability: Stainless steel hoses are known for their high tensile strength and ability to withstand harsh conditions, including high pressures and temperatures.
Superior Corrosion Resistance: Unlike aluminum, stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion, even in environments with aggressive chemicals or extreme temperatures.
Versatility in Applications: Stainless steel hoses can be used in a wide range of applications, from chemical processing to food and beverage industries, due to their hygienic properties and ability to withstand cleaning and sterilization processes.
4. Advantages of Stainless Steel Over Aluminum
Stainless steel quickly became the preferred choice for many industrial applications due to its numerous advantages over aluminum.
High Temperature and Pressure Tolerance: Stainless steel can withstand much higher temperatures and pressures than aluminum, making it ideal for high-performance applications.
Longer Lifespan: The durability and resistance to environmental factors contribute to a longer lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Enhanced Safety: Stainless steel hoses provide better safety due to their strength and resistance to leaks or ruptures, especially in high-pressure systems.
5. Technological Advancements in Hose Materials
The evolution from aluminum to stainless steel did not happen overnight. It was driven by continuous technological advancements and the need for more reliable and efficient hose solutions.
Development of Alloys: Advances in metallurgy led to the development of various stainless steel alloys, each tailored to specific industrial needs, further enhancing the versatility of stainless steel hoses.
Improved Manufacturing Techniques: New manufacturing techniques, such as seamless construction and advanced welding methods, improved the reliability and performance of stainless steel hoses.
6. The Future of Hose Materials: Beyond Stainless Steel
While stainless steel remains a dominant material in hose manufacturing, the search for even better materials continues.
Composite Hoses: The development of composite hoses, combining multiple materials, offers a balance of flexibility, chemical resistance, and strength.
Smart Materials: The future may see hoses incorporating smart materials that can self-heal, change properties based on environmental conditions, or provide real-time monitoring of flow and pressure.
Conclusion
The evolution from aluminum to stainless steel hoses represents a significant advancement in hose manufacturing, driven by the need for more durable, resistant, and versatile materials. Stainless steel hoses, with their superior properties, have set a new standard in various industries, ensuring safety, efficiency, and longevity. As technology continues to advance, the future of hose materials will likely see even more innovative developments, further enhancing their application and performance in industrial settings.