What Is a Vent Connector?
A vent connector is the short section of pipe that carries combustion gases from a heating appliance (such as a furnace or water heater) to the main venting system—usually a chimney or vent pipe.
It acts as the “bridge” that links the appliance outlet to the exhaust system.
A vent connector is not the same as:
- Vent Pipe – The main vertical pipe that carries gases outdoors.
- Exhaust Hose – Used for dryers and non-combustion appliances.
- Chimney Flue – The final exit route for combustion gases.
The vent connector is simply the connecting part between the appliance and the larger venting system.
What Does a Vent Connector Do?
1. Safely Carry Combustion Gases Away
The primary function of a vent connector is to move combustion by-products— including carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, moisture, and unburned fuel—out of your home and into the main vent system. A properly installed connector helps prevent dangerous gases from leaking into your living space, making it an essential safety component for any fuel-burning appliance.
2. Prevent Backdraft
Backdraft occurs when exhaust gases fail to exit the house and instead flow back toward the appliance or into the room. A vent connector maintains a stable, one-way airflow by using the correct slope, length, and connection angle. This helps ensure gases move in the right direction and reduces the risk of backdraft, protecting both indoor air quality and appliance performance.
3. Improve Venting Efficiency
A vent connector also plays a key role in the system’s overall venting efficiency. When it is properly sized, tightly sealed, and installed with minimal airflow resistance, it allows exhaust gases to move smoothly through the vent system. This leads to:
- More efficient fuel combustion
- Reduced energy waste
- Steadier appliance performance
- Lower maintenance needs
Poor installation—such as connectors that are too small, too long, or installed with excessive bends—can restrict airflow and reduce venting performance.
Types of Vent Connectors
1. Single-Wall Metal Connector
- Made from galvanized steel
- Affordable and easy to install
- Requires more clearance from combustibles
2. Double-Wall (Type B) Connector
- Inner aluminum lining + outer steel layer
- Better insulation
- Allows reduced clearance
- Safer for high-temperature exhaust
3. Flexible Aluminum Connector
- Bendable and easy to route
- Good for tight spaces
- Should not be over-compressed to avoid airflow restriction
4. Rigid Metal Connector
- Strong and highly durable
- Best for furnaces and long-term installations
- Provides stable airflow and minimal resistance
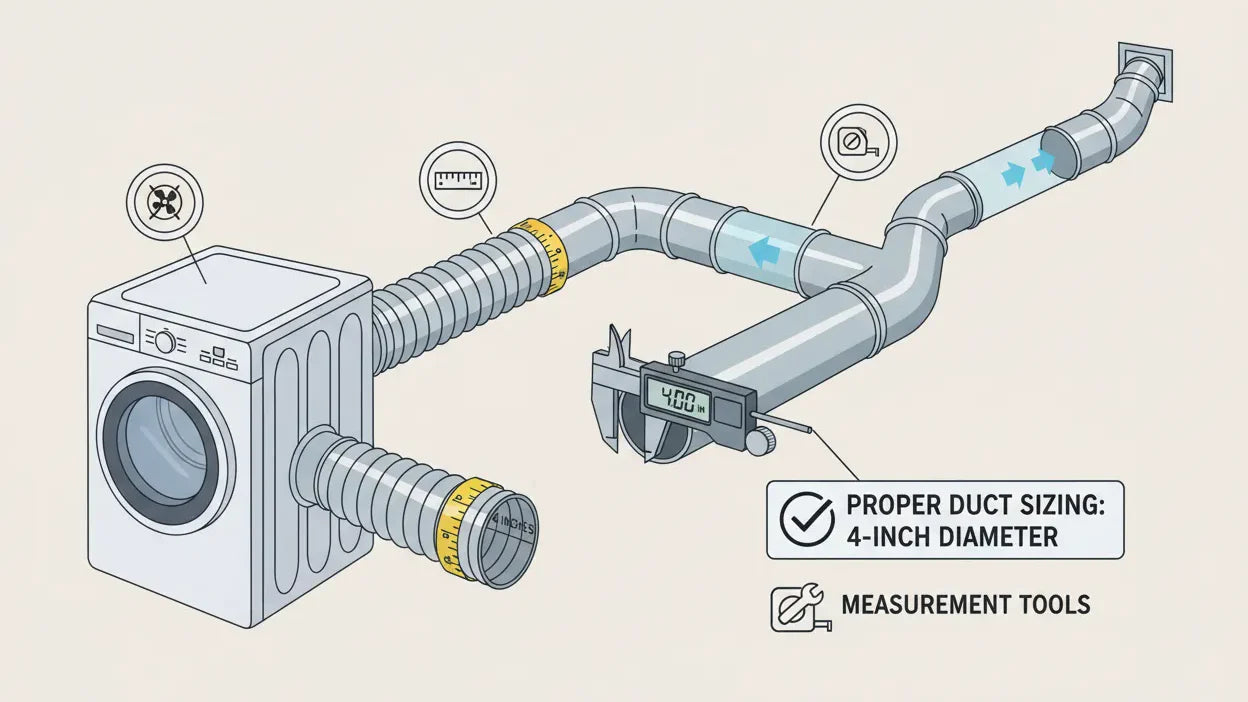
Common Vent Connector Sizes
The most common vent connector diameters include:
- 3-inch
- 4-inch
- 6-inch
To choose the right size:
- Measure the outlet diameter on the appliance.
- Match the vent connector diameter exactly—never downsize.
- Check manufacturer requirements and local codes.
How to Install a Vent Connector: Key Rules
1. Maintain Proper Slope
The vent connector must rise at least 1/4 inch per foot toward the vent or chimney. This prevents condensation buildup and backdraft.
2. Avoid Excessive Length
Long horizontal runs reduce draft. Follow local code requirements—shorter is always better.
3. Seal All Joints
Use foil tape, clamps, or mastic (if allowed). Do not use standard duct tape.
4. Keep Required Clearances
Single-wall connectors need more clearance from combustibles than double-wall connectors.
5. Support and Secure the Pipe
Use straps or brackets to prevent sagging, which can trap moisture.
Common Vent Connector Problems (and Fixes)
1. Connector Comes Loose
A vent connector can loosen over time due to the use of the wrong diameter, poor initial sealing, thermal expansion, or vibration from the appliance. A loose connector reduces draft strength and may allow combustion gases to leak into the home.
Fix: Replace the connector with the correct diameter, reseal all joints, and secure it with UL-listed clamps or sheet metal screws. Ensure all seams are airtight to maintain proper draft.
2. Moisture Leaks or Condensation
Condensation occurs when warm exhaust gases enter a connector that is improperly sloped, oversized, or poorly insulated. This moisture can lead to dripping, corrosion, and reduced venting efficiency.
Fix: Correct the slope so the connector rises toward the main vent, insulate the pipe if needed, or upgrade to a double-wall connector to minimize temperature loss and condensation.
3. Backdraft Issues
Backdrafting pushes harmful gases back toward the appliance or into the home. It is often caused by negative indoor pressure, long horizontal runs, poor draft, or a blocked main vent or chimney.
Fix: Shorten horizontal runs, increase vertical rise, and inspect the main vent for obstructions. Improving airflow or adding makeup air may also help in tightly sealed homes.
4. Noise or Rattling
Noise or rattling happens when the vent connector is not securely supported. Appliance vibration can shake loose or dent sections of pipe, eventually affecting system performance.
Fix: Add or tighten support brackets, secure all joints with proper screws, and replace any crushed or damaged sections to ensure smooth airflow.
When Should You Replace a Vent Connector?
Replace your vent connector if you notice:
- Rust or corrosion
- Holes or cracks
- Loose joints
- Improper slope
- Outdated materials
- Burn marks or heat damage
How to Choose the Right Vent Connector
When selecting a new vent connector, consider:
- Material – Metal is preferred for combustion appliances.
- Diameter – Match the appliance outlet exactly.
- Length & Flexibility – Rigid for stability; flexible for tight spaces.
- Heat Resistance – Check temperature rating.
- Accessories – Such as adapters, clamps, reducers, or elbows.
Conclusion
Vent connectors may seem like a small part of your HVAC, furnace, or dryer system, but they play a critical role in safely channeling exhaust gases out of your home. Understanding the different types, sizes, installation rules, and common issues can help prevent leaks, backdrafts, and other safety hazards. Always choose the right material, diameter, and length for your appliance, and follow local building codes for installation. With proper care and maintenance, a vent connector ensures your home stays safe, energy-efficient, and comfortable.